Google Earth Introduces Urban Heat Island Mapping for U.S. Cities
Introduction to Urban Heat Islands
The term urban heat island (UHI) refers to the phenomenon where urban areas experience significantly higher temperatures than their rural surroundings. This temperature disparity can be attributed to various factors, including the extensive use of concrete and asphalt, reduction of vegetation, and heat generated from vehicles and buildings. As cities across the United States grow, the impact of UHI becomes increasingly pronounced, affecting energy consumption, air quality, and overall public health.
Google Earth’s Innovative Approach
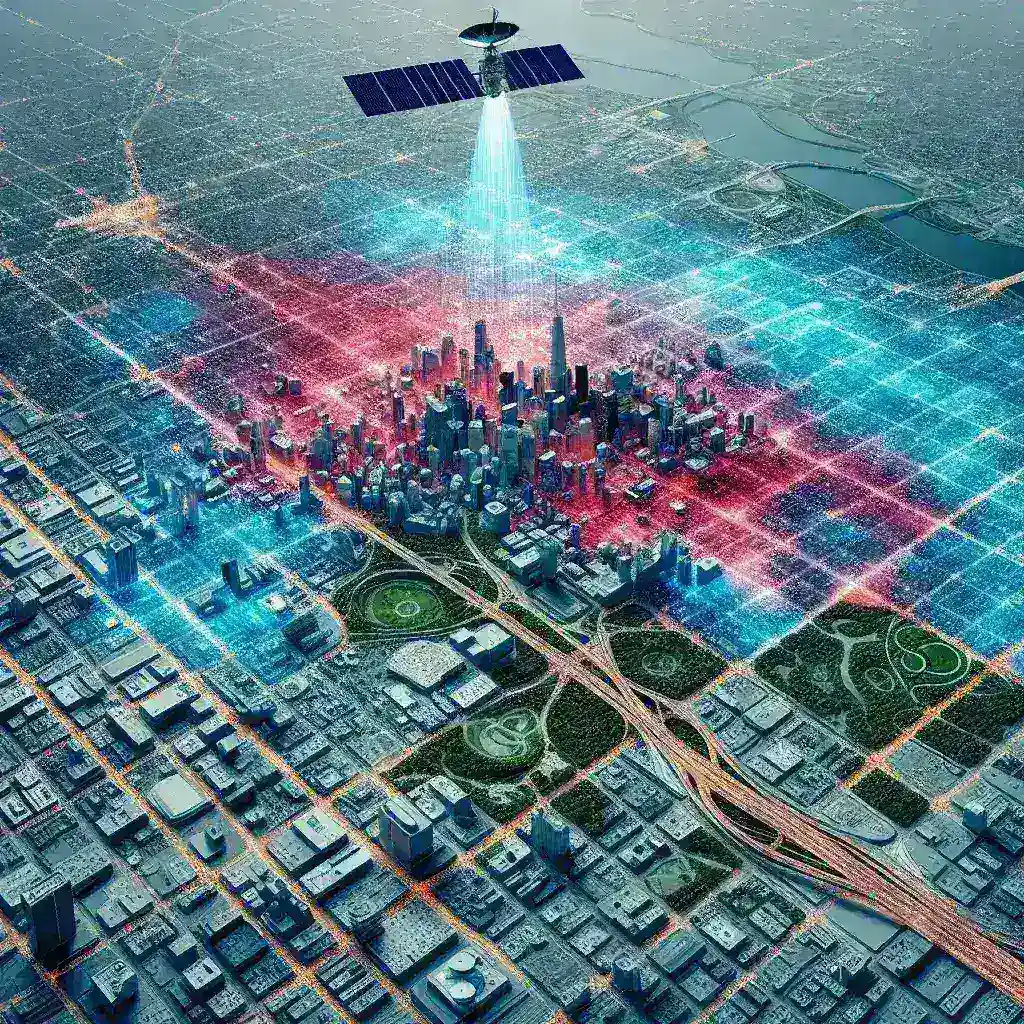
In an effort to address this pressing issue, Google Earth has introduced an innovative urban heat island mapping tool tailored specifically for U.S. cities. This tool enables users to visualize the intensity of UHI effects across different neighborhoods, offering a comprehensive picture of temperature variations. By leveraging satellite imagery and advanced data analytics, Google Earth aims to provide city planners, policymakers, and residents with actionable insights to mitigate these heat effects.
How the Mapping Tool Works
The urban heat island mapping tool utilizes high-resolution satellite imagery combined with historical climate data to create detailed thermal maps. Here’s a breakdown of how it functions:
- Data Collection: Google aggregates data from various sources, including satellite observations and weather stations, to gather temperature readings across urban areas.
- Visualization: The tool translates this complex data into easy-to-understand heat maps, highlighting areas that are particularly vulnerable to elevated temperatures.
- User Interaction: Users can interact with the map, zooming in on specific neighborhoods to view historical data trends and current conditions.
Historical Context of Urban Heat Islands
The concept of urban heat islands has been studied since the early 20th century. As cities expanded and the population grew, researchers began to document the temperature differences between urban and rural areas. In the years following World War II, rapid industrialization and urban development exacerbated the UHI effect, leading to increased concern among environmentalists and urban planners alike.
Recent Studies and Findings
Recent studies have reinforced the significance of addressing UHI, linking it to various health risks, such as heat-related illnesses and respiratory problems. For instance, a study conducted in 2020 found that neighborhoods with less vegetation and higher concentrations of asphalt were up to 7°F warmer than their greener counterparts. Such findings underscore the importance of urban planning that incorporates green spaces and reflective materials.
Implications for Climate Action
The introduction of urban heat island mapping by Google Earth has significant implications for climate action and urban resilience. As cities face the challenges of climate change, understanding local temperature dynamics becomes essential. Here are some ways the mapping tool can influence climate strategies:
- Informed Urban Planning: City planners can use the data to make informed decisions about where to plant trees, create parks, and implement cool roofs to combat UHI.
- Community Awareness: By making this data accessible to the public, communities can become more aware of their local climate challenges and advocate for solutions.
- Policy Development: Policymakers can create targeted initiatives aimed at reducing UHI effects, such as incentivizing green roofs or improving urban infrastructure.
Real-World Applications
Several U.S. cities have already begun to utilize the insights gained from urban heat island mapping to implement successful interventions. For example:
Los Angeles
In Los Angeles, city officials are using UHI data to prioritize tree planting in neighborhoods most affected by high temperatures. This initiative not only helps to cool the environment but also improves air quality and enhances the urban landscape.
New York City
New York has launched initiatives to convert rooftops into green spaces, supported by data that shows the most heat-affected areas. This approach aims to reduce energy consumption during peak summer months and improve urban biodiversity.
Future Predictions
As climate change continues to pose challenges for urban areas, the role of tools like Google Earth’s urban heat island mapping will become even more critical. Experts predict that:
- Increased Heat Events: The frequency and intensity of heatwaves are expected to rise, making UHI mitigation a top priority.
- Technological Advancements: Future iterations of the mapping tool may incorporate predictive analytics, allowing cities to anticipate UHI effects based on climate models.
- Global Adoption: Other countries may adopt similar mapping strategies, learning from U.S. cities to combat UHI on a global scale.
Pros and Cons of UHI Mapping
Pros
- Provides valuable data for urban planning and climate action.
- Facilitates community engagement and awareness.
- Helps identify areas in need of immediate intervention.
Cons
- Potential data privacy concerns with satellite imagery.
- Dependency on accurate data collection methods.
- May not capture microclimate variations within neighborhoods.
Conclusion
The launch of urban heat island mapping by Google Earth marks a significant step forward in understanding and addressing the challenges posed by urban heat in American cities. By providing critical insights into temperature disparities, this tool empowers city planners, policymakers, and communities to take proactive measures against UHI. As the impacts of climate change become more pronounced, innovative solutions such as this are essential for creating sustainable urban environments. The journey towards cooler cities is underway, and tools like these will pave the way for healthier, more resilient communities in the future.
Leave a Reply